Mark Kopec Now
Ulna Fracture
Injuries to the Ulna Bone: Treatment Options and Potential Bad Outcomes
Welcome to the Kopec Law Firm’s comprehensive guide on ulna fractures. This page aims to provide valuable information about the treatment options available for ulna bone injuries, as well as the potential bad outcomes that may arise during the treatment process. If you have been injured by treatment of an ulna fracture, you may have a medical malpractice claim and then need Baltimore ulna fracture lawyer Mark Kopec.
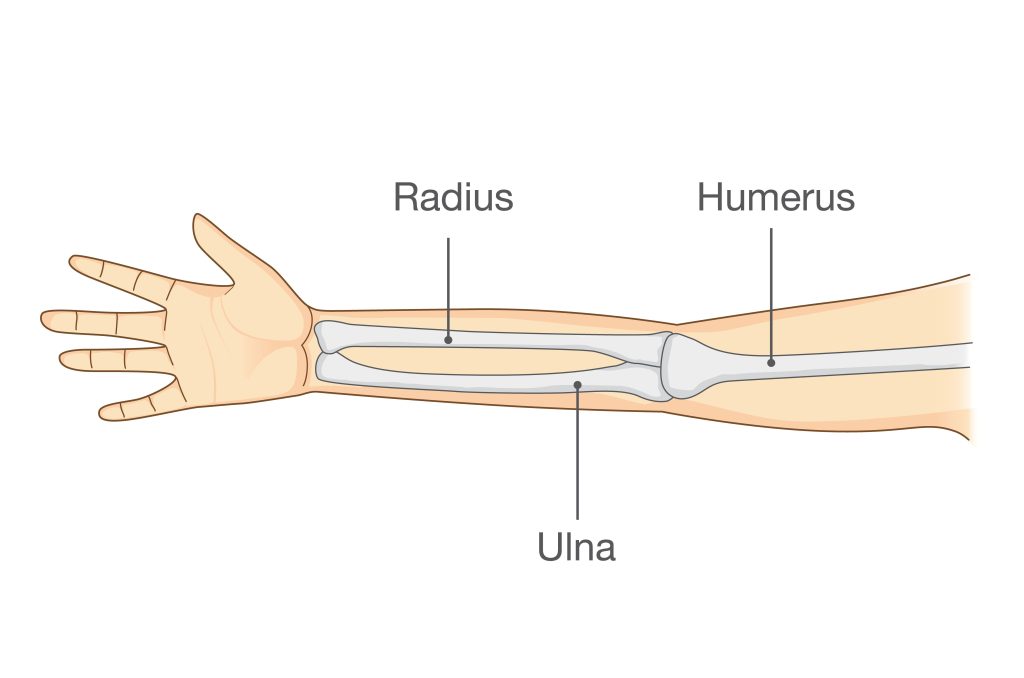
Overview of Ulna Anatomy
The ulna is one of two long bones in the forearm, the other being the radius. It’s located on the pinky-finger side of the forearm. The ulna extends from the elbow to the wrist and plays a crucial role in wrist and elbow joint function. Key anatomical features relevant to fractures generally include:
- Olecranon: The bony prominence at the back of the elbow. This is a common site for fractures.
- Coronoid Process: A projection that helps stabilize the elbow joint.
- Shaft (Diaphysis): The long, central part of the bone.
- Styloid Process: A small projection at the wrist end of the ulna.
Ulna fractures can occur in any of these locations and can range from simple, clean breaks to complex, comminuted (multiple fragments) fractures.
Doctors for Diagnosis and Diagnostic Tests
Several types of doctors can diagnose an ulna fracture:
- Emergency Room Physicians: Often the first point of contact for acute injuries.
- Primary Care Physicians (PCPs): Can initially assess the injury and refer to specialists.
- Orthopedic Surgeons: Specialists in bone and joint injuries.
- Radiologists: Interpret imaging studies.
Diagnostic tests used to identify and assess ulna fractures include:
- X-rays: The primary imaging method for diagnosing bone fractures, usually showing multiple views.
- CT Scans (Computed Tomography): Provides more detailed cross-sectional images, useful for complex fractures or when X-rays are inconclusive.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Less commonly used for initial fracture diagnosis but may be used to assess soft tissue damage (ligaments, tendons) associated with the fracture.
Doctors for Treatment
The primary specialists involved in treating ulna fractures are:
- Orthopedic Surgeons: Manage the fracture through various methods, including casting, splinting, or surgery.
- Physiatrists (Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Physicians): May be involved in post-fracture rehabilitation.
- Physical Therapists: Guide patients through exercises to regain strength, range of motion, and function after healing.
Treatment Options:
- Non-Surgical Treatment:
- Immobilization: In cases of minor fractures or non-displaced ulna bone injuries, immobilization using a cast, splint, or brace may be recommended. This allows the bone to heal naturally over time.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation during the healing process.
- Physical Therapy: Once the initial healing phase is complete, physical therapy exercises may then be recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This procedure involves realigning the fractured bone fragments and also securing them with screws, plates, or rods to promote proper healing.
- External Fixation: In complex fractures or cases with severe soft tissue damage, external fixation devices may stabilize the bone fragments from outside the body.
- Bone Grafting: In situations where there is a significant loss of bone or delayed healing, bone grafts may be utilized to specifically promote bone regeneration.
Potential Complications:
Bad outcomes can occur during the treatment of ulna bone injuries. Some potential bad outcomes may include:
- Infection: Surgical procedures carry a risk of infection, which can delay healing and require additional treatment.
- Non-union or Delayed Union: In some cases, the ulna bone may not heal properly, leading to non-union or delayed union. This may require further intervention, such as revision surgery or bone stimulation techniques.
- Nerve Damage or Blood Vessel Damage: During surgical procedures, there can be nerve or blood vessel damage, which can result in numbness, weakness, or impaired blood flow.
- Hardware Complications: Implants used during surgery, such as screws or plates, may cause irritation, discomfort, or require removal if they become problematic.
- Stiffness or Reduced Range of Motion: In certain cases, stiffness or limited range of motion may persist even after successful treatment. Physical therapy and rehabilitation can help address these issues.
Medical Malpractice with Baltimore Ulna Fracture Lawyer Mark Kopec
Complications from treatment of ulna fractures may constitute medical malpractice. Medical malpractice occurs when a healthcare professional deviates from the accepted standard of care, resulting in harm to the patient. Determining medical malpractice requires a thorough evaluation of the specific circumstances and expert opinion.
Potential Medical Malpractice Claims Related to Ulna Fractures
Medical malpractice claims related to ulna fractures could potentially arise from the following situations:
- Misdiagnosis or Delayed Diagnosis: Failure to recognize a fracture on imaging studies or misinterpreting the type of fracture, leading to improper treatment and worsened outcomes.
- Improper Treatment:
- Incorrect casting or splinting leading to malunion (improper healing) or nonunion (failure to heal).
- Surgical Errors, such as nerve damage, improper placement of hardware, or infection.
- Failure to recommend or perform necessary surgery.
- Inadequate Post-operative Care: Failure to monitor for complications, provide appropriate rehabilitation protocols, or address patient concerns.
- Failure to Obtain Informed Consent: Not properly explaining the risks, benefits, and alternatives of treatment options to the patient.
Next Step: Call Baltimore Ulna Fracture Lawyer Mark Kopec
Injuries to the ulna bone can vary in severity, and treatment options depend on the specific case. Bad outcomes can arise during treatment. Establishing medical malpractice requires demonstrating that a medical professional’s actions fell below the accepted standard of care and also directly caused harm to the patient. Consequently, it is crucial to consult with a qualified medical malpractice attorney to evaluate the specific circumstances of a potential claim. We will investigate the medical records, consult with medical experts, and determine if there are grounds for a lawsuit.
Visit our free consultation page or video. Then contact the Kopec Law Firm at 800-604-0704 to speak directly with Attorney Mark Kopec. He is a top-rated Baltimore medical malpractice lawyer. The Kopec Law Firm is in Baltimore and pursues cases throughout Maryland and Washington, D.C.





